Statistics on Occupational Injuries from Electrical Incidents
In 2021, the average number of electrical accidents in Malaysia is at 52 cases yearly. According to the Energy Commission (EC), the majority of these accidents were contributed by the usage and handling of uncertified and faulty electrical appliances. We feel sorrowful for the recent electrocuted incident that happened to a 21-year-old worker on Aug 5, 2022.
New Straits Times: https://www.nst.com.my/news/nation/2022/08/821194/worker-electrocuted-selangor-osh-probes-incident-port-klang-company

Source of image: canva.com
Adolescents and adults are prone to high voltage shock caused by mischievous exploration and exposure at work. About 1,000 people in the United States die each year as a result of electrocution. Most of these deaths are related to on-the-job injuries.
Definitions of Electric Shock & Electrocution
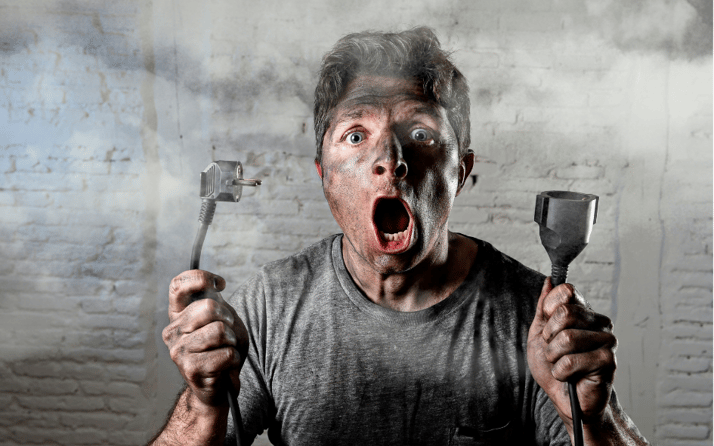

Source of image: canva.com
Electric shock (n): Collins dictionary defines electric shock as a dangerous and painful physiological effect caused by the passing of an electric current through the body of a human or animal. Exposure to electrical energy may result in no injury at all or may result in devastating damage or death.
Electrocution (n): Electrocution is death or severe injury caused by electric shock from electric current passing through the body. The word is derived from "electro" and "execution", but it is also used for accidental death.
The Possible Consequences of an Electric Shock on Human Body
Without proper electrical protection, any electricity current can easily travel through the human body due to the good electrical conductivity of the human body. This then leads to electric shock or even more serious, fatal electrocution.
- Muscle Spasms
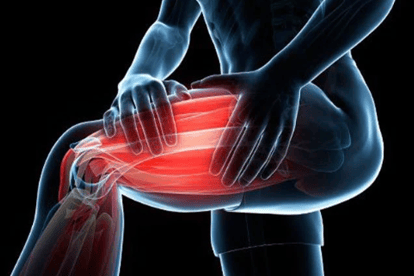 Source of image: emedicinehealth
Source of image: emedicinehealthSince muscle contractions are stimulated by electricity, the effect from an electric shock depends on the intensity of the current and the type of muscle it travels through. For examples, a current as low as 0.25 milliamperes (mA) would not cause injury but just a sense of buzzing or tingling; a sustained contraction can be caused when a current above 10 mA travels through flexor muscles, like the ones in our forearms that responsible for the movements and contractions of fingers. This can lengthen the duration of the electrical contact and further increase the severity of the shock as the victim may be unable to let go of the source of current; when the same level of current above 10mA passes through extensor muscles, it causes a violent spasm. The victim might be propelled metres away if the affected muscles are hip extensors. Moreover, muscles, ligaments, and tendons may tear as a result of the sudden contraction caused by an electric shock. Tissue can be burned by the shock of high or lasting current.
- Cardiac Arrest
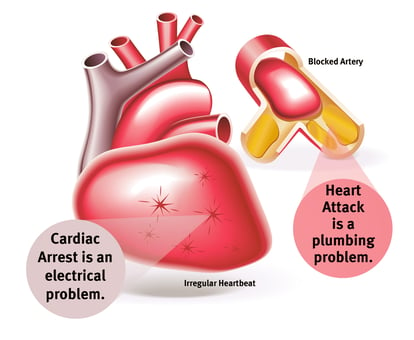 Source of image: Luminis Health
Source of image: Luminis Health
Cardiac arrest can happen when a current of 50 mA passes through the heart. Heart is formed by a specialized muscle tissue named cardiac muscle tissue, or myocardium, which contract involuntarily to pump blood throughout the body. As we can observed through electrocardiogram, the rhythm of our heartbeat is controlled by electric impulses. An external current can mask these impulses and disturb the heart’s rhythm and cause irregular heartbeat, called arrhythmia and can even manifest ventricular fibrillation (a total disorganization of the rhythm). Arrhythmia can happen immediately at the time of shock or a few hours after the electric shock. The heart stops pumping and the blood can no more be circulating throughout the body when ventricular fibrillation occurs. This can cause death if a normal heartbeat is not restored with defibrillator.
- Burns to Tissues and Organs
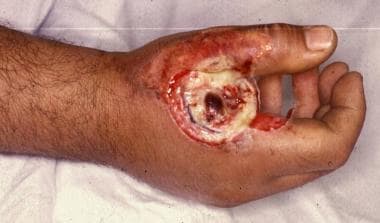
Source of image: Medscape
A current above 100mA leaves marks at the points of contact with the skin when it passes through the body. Serious burns that may require amputation of the affected limb can be caused by currents above 10,000 mA (10 A). Some burns look similar with thermal burn. Even tiny charred craters that seems harmless indicate the presence of much more severe internal burns. Internal damage that affect internal organs may be much more serious than the external injuries suggest. This is because, internal burns often led to serious effects: scarring, loss of sensation, loss of function, amputation, and even death. Besides, the large amount of waste generated from the large number of damaged tissues can give rise to serious kidney or blood circulation disorders.
- Affect the Nervous System
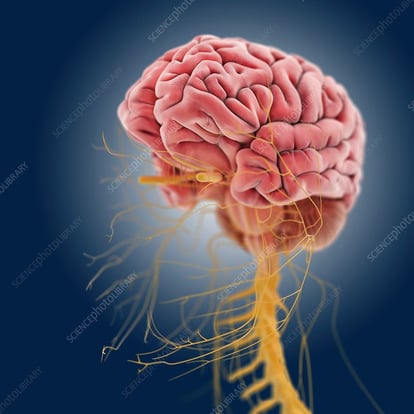
Source of image: Science Photo Library
Nerves are tissues that have very little resistance to electrical passage. When an electric shock happened on the nerves, the victim may suffers from temporarily or permanent effects such as pain, tingling, numbness, difficulty in movements. An electric injury on the central nervous system can bring the victim to dazed, amnesia, seizure or even respiratory arrest. Psychiatric disorders can be resulted when long-term damage to the nerves and the brain occurred.
- Other unexpected Consequences
Other disorders can appear in the following weeks or months after the shock, depending on the affected body organs. For example, cataracts may develop over time if the current accidentally passed through the eyes.
What is PPE: Definition of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)

Source of image: canva.com
Protection of employees’ safety and health should be prioritised by every employer as the workers might be at risk of exposing themselves to many types of hazardous situation due to the nature of work involved. According to the Department of Occupational Safety & Health (DOSH) Malaysia, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), is any equipment which is intended to be worn or held by a person at work and which protects him/her against one or more risks to health or safety and any additional accessory designed to meet that objective. Personal protective equipment has been used since ancient times to give protection to the wearer against harmful elements. The use of personal protective equipment is the only practicable protection in certain circumstances. Therefore, these equipment must be properly selected, used, and maintained to provide adequate protection to the wearer.
Approval of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is one of the needs and requirements of the Factories and Machinery Act 1967, Occupational Health and Safety Act 1994 and Regulations there under. All PPE should have a full type test report and product certification license from Independent Inspecting/ Certification Body appointed by DOSH which is SIRIM Qas International Sdn Bhd.
Basic PPE for Electrical Protection and Safety

Source of image: canva.com
The best way to keep people safe from electrical hazards in the workplace is by implementing policies and procedures that reduce or eliminate various risks. Unfortunately, it is impossible to take steps that can be 100% effective, and if there is even one incident it can be deadly. With this in mind, it is important that anyone working with or around dangerous electrical equipment use personal protection equipment to keep them safe in the event of an accident. The following are among the most frequently used types of PPE, and how they can keep your workplace safer.
- Insulated Gloves– Insulated gloves will prevent electricity from traveling into your hands should there be an exposed wire, short circuit, or other issue.
- Insulated Matting– Insulated matting will put a protective layer between the employee and the floor. This is helpful when working at switchboards, transformers, and other high-voltage areas. It can help prevent electricity from traveling up from the floor into the person’s body, as well as eliminating a path for electricity to travel through the body and out to the floor.
- Insulated Ladders– Insulated ladders won’t transmit electricity into the person who is using it. If a normal metal ladder accidentally touches a live electrical wire, it can be devastating. With the insulated ladder, this isn’t an electrical concern.
- Rescue Rods– In the event that someone is being electrocuted, people will be tempted to rush in to save them. Unfortunately, this will only lead to them becoming electrocuted as well. Having a rescue rod present will allow those in the areas to pull the victim to safety, or push the source of the electricity away.
- Voltage Detectors– Even after a power source has been removed, there can still be electricity in a system because of capacitors. A voltage detector will show the level of electricity in a given system at the current time, so employees won’t mistakenly begin working on a system until all power has been eliminated.
Options for PPE
Each piece of personal protection equipment will be rated for different levels of electrical current. The more powerful the electricity, the more insulated or protected the equipment needs to be to keep employees safe. Wearing the wrong PPE can be just as dangerous, or even more so, than wearing no PPE because it can give a false sense of safety. Make sure you have the proper equipment for a given environment to get the best possible results.
Not Sure Which PPE to go for? Contact Us Now For a FREE Consultation!

Source of image: canva.com
SAFETYWARE manufactures products like safety shoes and boots, safety apparel, hygiene and sanitization items, medical masks and signage with advance European machineries under stringent quality control system certified to ISO 9001:2015 Standard and certified to CE, ASNI, AS/NZS, SIRIM, Singapore Standard, etc. When it comes to occupational safety & health, rest assured that you can count on Safetyware Group - an award-winning integrated safety & health solutions provider with close to 20 years of experience. Backed by a team of professionals who are committed and passionate, we always work closely with each unique customer to provide the best possible solution whenever and wherever they are needed. Value-added services like technical assistance and support are also part of our promises to make sure products are properly and appropriately used for a longer life span, avoid unnecessary injuries due to improper usage, better protection for your end products from contamination, and help to save your money at the end of the day.
Dielectric Glove Electrical Testing:
Safetyware offers full service testing and re-certification of Dielectric Rubber Gloves. Our partner's facility in USA is equipped with state-of-the-art equipment for the completed testing of Dielectric Rubber Gloves, including washing, visual inspecting, and electrical testing. The Dielectric Rubber Gloves must be periodically tested to ensure the products maintain their integrity when exposed to a full range of voltages. If the gloves does fail during testing, a new, certified Dielectric Rubber Gloves should be prepare to replacement.





